Introduction to Sole Proprietorship Regulations
Starting your own business can be an exciting venture, but it’s crucial to understand the legal requirements and sole proprietorship regulations before diving into the entrepreneurial world. As one of the most common and simplest business structures, a sole proprietorship is a popular choice for many entrepreneurs. In this article, we will explore the sole proprietorship regulations, what they mean for business owners, and how to ensure compliance with the law.
What Is a Sole Proprietorship?
A sole proprietorship is a business owned and operated by a single individual. It’s the easiest and least expensive business structure to set up, making it an attractive option for many small business owners. The owner assumes full responsibility for all aspects of the business, including its debts, liabilities, and taxes. However, with the flexibility comes the need to follow specific sole proprietorship regulations to ensure legal compliance.
Also Read: Fake Identity Cases
Why Choose a Sole Proprietorship?
There are many reasons why entrepreneurs opt for a sole proprietorship. Some of the benefits include:
- Simple Setup: The sole proprietorship regulations allow for easy registration and minimal paperwork.
- Full Control: As the sole owner, you have complete control over business decisions.
- Tax Benefits: Profits and losses are reported on your personal tax return, making it easier to file taxes.
Understanding Sole Proprietorship Regulations
While setting up a sole proprietorship is relatively straightforward, there are several sole proprietorship regulations that you must adhere to. These regulations vary depending on your location and industry, but some common rules apply universally.
- Business Name Registration: Depending on your jurisdiction, you may need to register your business name. If you’re using a name other than your own personal name, a “Doing Business As” (DBA) registration might be required.
- Licenses and Permits: Many businesses require specific licenses or permits to operate legally. These could include local business licenses, health department permits, or professional certifications.
- Tax Requirements: Sole proprietors must comply with various tax regulations, including income tax, self-employment tax, and sales tax if applicable. The sole proprietorship regulations typically require you to report all income and expenses on your personal tax return using Schedule C (Form 1040).
- Zoning Laws: If you’re running a business from home or a physical location, you’ll need to ensure your business complies with local zoning regulations. Zoning laws govern the type of business that can operate in certain areas.
- Insurance and Liability: Unlike corporations or limited liability companies (LLCs), a sole proprietorship does not provide personal liability protection. Business owners are personally liable for any debts or legal issues that arise. It’s advisable to consider liability insurance to protect your personal assets.
- Employment Regulations: If you hire employees, you must comply with employment laws, including workers’ compensation, unemployment insurance, and payroll taxes.
Steps to Start a Sole Proprietorship
Starting a sole proprietorship requires several steps to comply with sole proprietorship regulations and to ensure that your business runs smoothly. Here’s a step-by-step guide to getting started:
- Choose Your Business Name: Select a name for your business. Make sure it complies with the regulations in your state and is not already in use by another business.
- Register Your Business: In many areas, you’ll need to register your business with the appropriate local or state authorities. This can often be done online.
- Obtain Necessary Permits and Licenses: Research the specific licenses and permits required for your business type. This could range from general business licenses to industry-specific certifications.
- Apply for an Employer Identification Number (EIN): While an EIN isn’t always required for sole proprietors, it can help separate your personal and business finances and streamline tax reporting.
- Open a Business Bank Account: It’s crucial to keep your personal and business finances separate. Open a business bank account and use it for all business transactions.
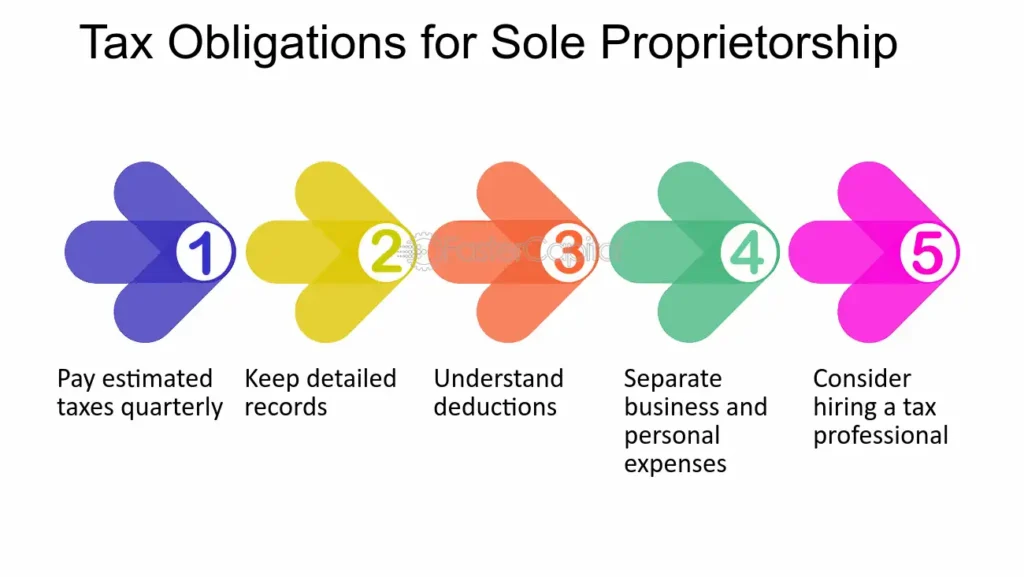
- Comply with Tax Laws: Make sure you understand the tax obligations associated with your sole proprietorship. This includes income tax, self-employment tax, and possibly sales tax.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Starting a Sole Proprietorship
Although starting a sole proprietorship is straightforward, there are common pitfalls that many entrepreneurs face. Here are a few mistakes to avoid:
- Not Understanding Tax Obligations: Sole proprietors must file taxes as individuals. Failing to understand your tax responsibilities can lead to fines and penalties. Make sure you keep accurate records of your business income and expenses.
- Not Insuring the Business: Many sole proprietors neglect to purchase business insurance, leaving their personal assets vulnerable to lawsuits or claims. Always consider liability insurance to protect yourself.
- Mixing Personal and Business Finances: It’s important to keep your business and personal finances separate to maintain accurate records and avoid legal complications. Open a business bank account and use it exclusively for your business transactions.
The Advantages of Sole Proprietorship Regulations
Choosing a sole proprietorship comes with many benefits, especially when it comes to simplicity and control. Here are some advantages:
- Minimal Paperwork: The sole proprietorship regulations generally require less paperwork compared to other business structures like LLCs or corporations.
- Tax Simplicity: Sole proprietors report business income and expenses on their personal tax return, making it easier to file taxes.
- Complete Control: As the sole owner, you have full control over all decisions, from business strategy to finances.
The Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship Regulations
However, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
- Unlimited Liability: Unlike corporations or LLCs, sole proprietors have unlimited personal liability for business debts and legal claims.
- Limited Growth Potential: Sole proprietorships are limited in terms of raising capital and expanding the business.
- Difficulty in Succession: A sole proprietorship often ends when the owner retires, dies, or chooses to close the business, which can make succession planning difficult.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the key sole proprietorship regulations I need to follow?
A1: The key regulations include registering your business name, obtaining necessary licenses and permits, complying with tax obligations, and ensuring that you have the proper insurance coverage.
Q2: Do I need to file taxes separately for my sole proprietorship?
A2: No, as a sole proprietor, you file taxes on your personal tax return. You will report your business income and expenses on Schedule C (Form 1040).
Q3: Can I hire employees as a sole proprietor?
A3: Yes, you can hire employees as a sole proprietor. However, you must comply with employment laws, including payroll taxes, workers’ compensation, and unemployment insurance.
Q4: Is a sole proprietorship the best choice for every business?
A4: A sole proprietorship is ideal for small businesses with limited liability risks. However, if you plan to scale or face potential lawsuits, you might want to consider an LLC or corporation for additional legal protection.
Q5: How do I protect myself legally as a sole proprietor?
A5: While sole proprietorships do not offer liability protection, you can minimize risks by purchasing business insurance, keeping personal and business finances separate, and maintaining proper contracts and documentation.
Conclusion
Understanding sole proprietorship regulations is crucial for anyone considering this business structure. While it offers many benefits, such as simplicity and control, it also comes with specific legal responsibilities and risks. By following the necessary regulations and taking steps to protect your business, you can enjoy the advantages of a sole proprietorship while minimizing the challenges.